

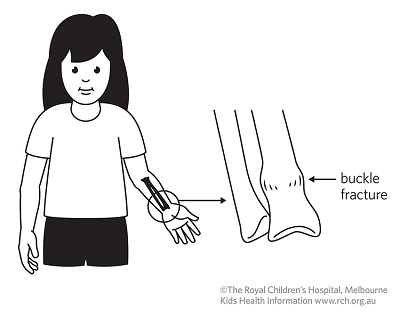
There is rarely any problem with healing and the children can do all the things they did before. Your hand therapist at Action Rehab will be able. John just needed a cast.īuckle fractures usually heal very quickly and very nicely. More-severe greenstick fractures may cause an obvious deformity, accompanied by significant pain and swelling. If it does need to be straightened, it can be a bit difficult, due to the strong periosteum. What is a buckle fracture Your child has suffered a ‘buckle’ fracture of their arm and wrist. If a buckle fracture of the radius has only a little bend (depending on age, 10 to 20 degrees), it does not need to be reduced (bent back straight).
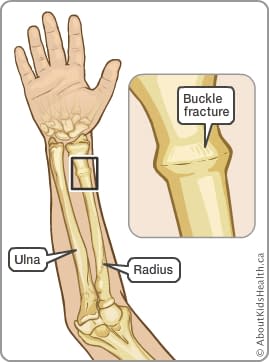
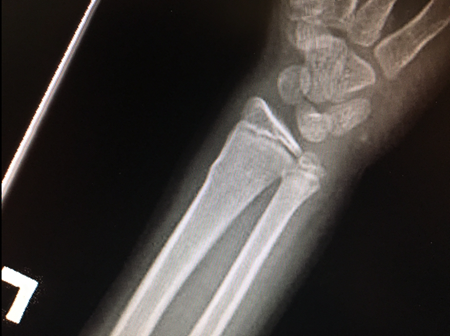
This is usually not torn and holds the bones in place. In addition, the layer of soft tissue over the bone, called the periosteum (which means the "tissue around the bone"), is quite thick and strong. When the bones of a child are stressed more than they can tolerate, they can buckle (which means bend) or deform like a green stick. The bones of children are still growing and are not as brittle as the bones of adults. This fracture is called a buckle fracture or a greenstick fracture. The large bone on the left is called the radius, the other bone is called the ulna. This is a close-up view of the wrist area. There is only a small bending of the cortex (outer part) of the bone. Surgical repair of pediatric hand and wrist fractures is rarely required in situations where the bone cannot be set straight or if it not healing properly with cast treatment.The fracture is indicated by the red arrows. Sometime the fracture will need to be “set” straight before splinting. Delayed treatment of pediatric fractures can lead to undesirable outcomes including malunion (bone doesn’t heal straight), and nonunion (bone doesn’t heal at all).Īnd casting are the mainstays of nonoperative treatment for fractures that are stable and not badly displaced (out of alignment). Even without these warning signs, it is best to seek urgent treatment so that the fracture can be set straight and Or “tight” swelling, significant deformity, or any open wounds around the hand or wrist (possible open or compound fracture). Suspected hand and wrist fractures warrant emergent treatment if your child is experiencing hand numbness and tingling, severe Yes! Some fractures are obvious if there is a deformity, but typically X-ray is used to definitively diagnose the fracture and plan treatment. Is There a Test for Hand and Wrist Fractures?
Elevate your wrist above the level of your heart as often as possible. Ice helps prevent tissue damage and decreases swelling and pain.
Cover it with a towel before you place it on your skin. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Finger hyperextension / jamming injuries Apply ice on your wrist for 15 to 20 minutes every hour or as directed.Direct blows to the hand or wrist (sports, vehicle accidents).Fall onto an outstretched hand (most common).Most hand and wrist fractures in children are caused by injuries: The fractures occur around the soft growth plates at the wrist and bases of the fingers. Because children’s bones are more flexible than adults’, sometimes they “bend” or “buckle” like a “green stick” rather than cracking. These are all just different ways of describing a fracture. You’ve been told the bone was “broken”, “hairline”, “green stick”, “buckled”, “cracked”, “chipped”, “split”, “shattered”, or “splintered”, Fractures are simply breaks or cracks in the bone. Unfortunately, fractures are a right-of-passage for most children. Of all ages, and when they land on their outstretched hand or wrist, injuries can occur. Kids are active, but not always graceful! Falls happen to children What Are Pediatric Hand and Wrist Fractures?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
